Deploying Kanzi applications to Android¶
Building and deploying Kanzi applications from Kanzi Studio¶
In Kanzi Studio you can build and deploy your Kanzi application to an Android device using a single command. This approach is useful when you want to see how your application works and looks on an Android device while you are still prototyping or developing your application.
Note
The first time you build and deploy an Android package, you need to have a working Internet connection because the build process downloads and installs the Android Gradle build system.
Note
When you build and deploy a Kanzi application created with the Kanzi Studio project template, Kanzi exports the Android package to the <KanziWorkspace>/Temp directory. See Creating a project.
To build and deploy Kanzi applications from Kanzi Studio:
Connect your Android device to your computer.
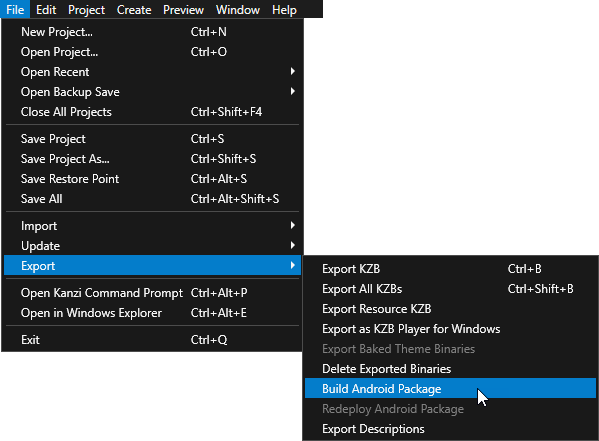
In Kanzi Studio create or open the project for your Kanzi application and select File > Export > Build Android Package.
Kanzi Studio builds the application source code, creates the .apk package, and installs the package to your Android device.
Configuring Android builds¶
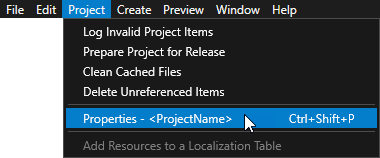
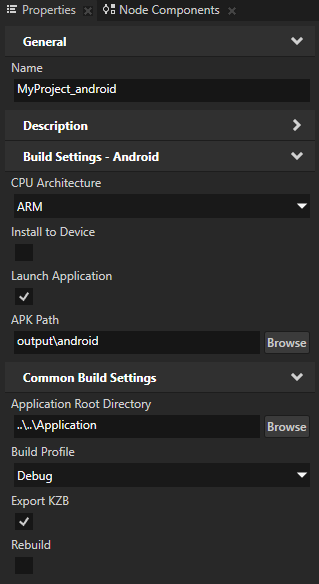
You can configure the building of your Kanzi applications for Android using the application configurations in Kanzi Studio. For example, you can set the target architecture, and whether Kanzi should deploy the built package to the attached target device. You can set which application configuration you want to use when you select File > Export > Build Android Package in Project > Properties in the Default Build Configuration property.
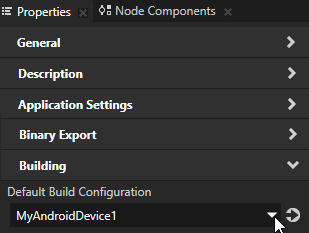
In Kanzi Studio in the Library press Alt and right-click Build Configurations and select Android Build Configuration.
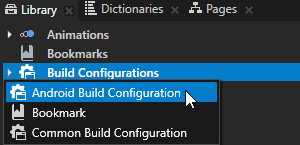
In the Properties set the configuration for the Android build.
For example:
Set the Build Profile property to Debug to build using the debug build type, instead of the default Release build.
Disable the Install to Device property if you want to manually install the .apk package to your Android device.
Building and deploying Kanzi applications from Android Studio¶
To build and deploy Kanzi applications from Android Studio:
Open Android Studio and in the Welcome screen select Open an existing Android Studio project.
The Open File or Project window opens.

In the Open File or Project window go to
<ProjectName>/Application/configs/platformsand select theandroid_gradleproject.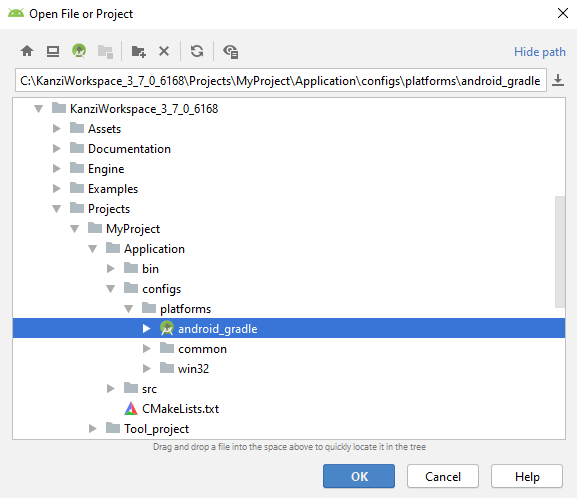
In Android Studio in the main menu select Build > Make Project to build the application package.
By default Android Studio uses the debug build configuration. When you build the Kanzi project, you can find the Android package at
<ProjectName>/Application/configs/platforms/android_gradle/app/build/outputs/apk/debug.To build using the release build configuration, open the Build Variants window and set the Build Variant to release.

Tip
If you do not specify the target architecture, Gradle builds the package for all supported platforms. You can set the architectures for which you want to build your package in
build.gradle.android { defaultConfig { ndk { abiFilters 'arm64-v8a', 'x86' } } }
Deploy your Kanzi application to an Android device or an Android Virtual Device:
Connect your Android device to your computer. To deploy to an Android Virtual Device, you must create one. See https://developer.android.com/studio/run/emulator.
In the Android Studio main menu select Run > Run 'app' and select the device to which you want to deploy your application.

Building and deploying Kanzi applications from the command line¶
You can build and deploy your Kanzi application to an Android device using the command line. In the <ProjectName>/Application/configs/platforms/android_gradle directory of your project:
To build an Android package, run one of these commands depending on whether you want to use the release, profiling, or debug build type:
gradlew assembleRelease
gradlew assembleProfiling
gradlew assembleDebug
If you do not specify the target architecture, Gradle builds the package for all supported architectures. However, you can build the package only for a specific architecture.
For example,
To build for ARM, run:
gradlew assembleRelease -Parch=arm
To build for multiple specific architectures, separate the architecture names with a comma:
gradlew assembleRelease -Parch=arm,aarch64,x86
To install an Android package on a device, run:
gradlew assembleRelease installRelease
To deploy an Android package on a device, run:
gradlew startPackage
To clean old Android package builds, run:
gradlew clean cleanNative
Stripping debug symbols¶
When you build your application for production, to reduce the binary size, you can strip the debug symbols from the native libraries of your application. To do this, pass the stripNativeLibs property:
gradlew assembleRelease -PstripNativeLibs
Note
A bug in the Android Gradle plugin does not allow you to enable this option by default for a particular build variant. See https://issuetracker.google.com/issues/155215248.